Exclusive mode in Windows
For lower sound system latency, exclusive access via WASAPI interface is used by default. It has to be enabled in microphone and headphones properties in Control panel.
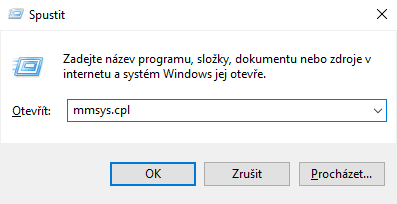
For opening the needed dialog press Win + R, write
mmsys.cpl into the field for command to be opened, and
press Enter.
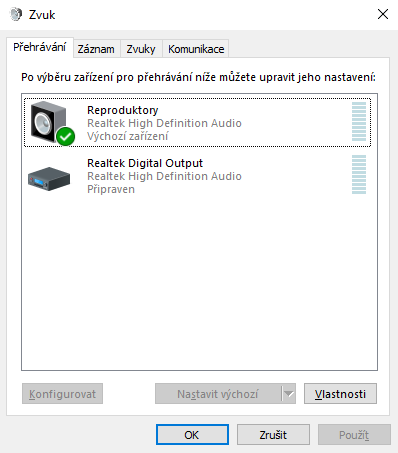
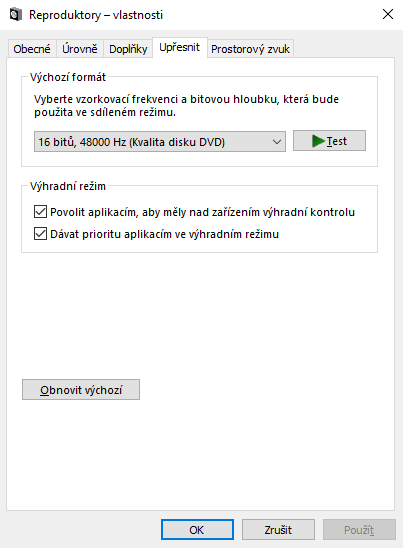
For both microphone and headphones click on the Properties button and on the Advanced tab
- set Default Format to 16 bit, 48 000 Hz,
- check Allow applications to take exclusive control of this device, and
- check Give exclusive mode applications priority.
Microphone volume and boost
On the way from your microphone to the remote headphones the sound volume is adjusted on several places and wrong setting on whichever of them may cause problems.
On the microphone side, we can usually set
- microphone boost on its input to computer,
- system microphone volume, and
- microphone volume within the application.
These settings may seem interchangeable, but they aren’t.
System boost and volume may be usually set on Linux by an
alsamixer app, on Windows it is on the tab
Levels in the same dialog as Exclusive mode was set.
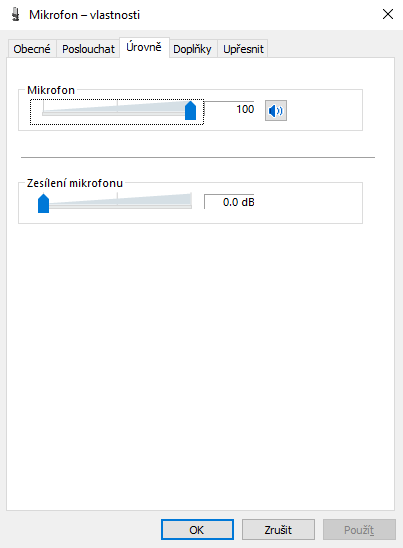
First of all, set system microphone volume to 100 % and boost to 0
dB. Then find out, to which maximum values system level in
the third step in the application goes when singing loudly:
-78 -20 -10 0 | |
| | | | V V
system level: [######++++----------------------------] -65 dB (-57 dB)
adjusted level: [############++++----------------------] -52 dB (-45 dB)If the + symbols exceed -10 dB, lower the system volume,
to get it just under this value. In case of creaking of loud tones, it
may be better to move your microphone to greater distance, instead of
lowering the volume.
If on the other hand the + symbols are still under -20
dB, increase microphone boost slightly.
After setting the volume on system level scale, press
r in the application to reset in-application
adjusted level of volume. Sing loudly to set that level
again.
A minor corrections of the adjusted level are possible
after connecting by pressing +/-.
Wrong settings may cause the following issues:
- low
system level– noise/buzzing; - high
system level– cutting/creaking of loud tones; - high boost and low system volume – combination of the previous two
symptoms, even with correct value of
system level; - high
adjusted level– louder than other voices, cutting/creaking; - low
adjusted level– lower volume than other voices.
Choosing audio device
Just after running the application, you can select your sound device
with c key. The same device may be shown in the list
multiple times with different sound interfaces. Choosing the right
interface may influence both latency and whether you can hear sounds
from other applications while using this one.
The list of some interfaces:
- Windows:
- WASAPI in exclusive mode is the default, it has latency about 30 ms (input+output).
- WASAPI in shared mode may have latency over 50 ms, but allows mixing sounds with other applications.
- ASIO might have even lower latency than WASAPI, but setting it is more complicated and not tested.
- …
- Linux:
- PulseAudio is the default, latency may be 20–30 ms,
- Alsa provides an exclusive access to the device for one application at a time, latency is 10–20 ms, PulseAudio should be turned off beforehand,
- JACK allows sound mixing with similar latency as Alsa (not tested).
- …
- MacOS:
- (supported interfaces were not much tested)
The presented times are only indicative, some devices may have even by tenths of ms higher latencies.
WiFi connection optimization
The application is highly sensitive to the stability of the internet connection incl. low jitter, which cannot be guaranteed when using wireless connection – cable connection is thus always preferred. WiFi may be sometimes also usable, see following tips.
For WiFi diagnostics install an application for signal strength measurement to your mobile phone, it may be called for example WiFi Analyzer.
Besides the signal strength of your WiFi at different places, you will also find out its interference with other networks which use the same channel. WiFi access points usually use one of the 14 channels on 2.4 GHz and at the same time one of many channels on 5 GHz – you need to check both, unless you know which one you are using.
If you can choose which frequency should be used, 5 GHz is usually better. The connection is there faster and more stable and thanks to greater number of channels, the interference with other networks and microwave ovens is not so common. The signal on 2.4 GHz can, however, better pass through walls, so it may be better if the access point is in another room.
You can change the network channel in your router settings, or even disable using 2.4 or 5 GHz if needed.
You can get to the router settings by entering an IP address of your default gateway to your web browser; you can find it in network properties – usually it is 192.168.0.1 or 10.0.0.1. If nobody has taken care about network security, you may try to login there by the following pairs of name and password: (admin, admin), (Admin, Admin), (root, root), etc. It may also be written on the router.
If the router has external antennas, you may try changing their direction. The strongest signal is orthogonally to them; the lowest signal is in the direction there are pointing to.
You can also try to disconnect from the network and connect there again; it may cause switching between 2.4 and 5 GHz.
Application performance optimization
To achieve low latency, the application needs to get access to the cpu at least once per 2.67 ms, which requires more precise timing than is usual. This regularity may be disrupted for example by the system’s effort of saving energy or by using multiple applications at the same time. It may then result in more frequent glitches during connection.
So if you have any application for energy saving, switch it to the performance mode. It may be also activated automatically when running from battery, so even connecting your laptop to AC may do the trick.
It is also possible to increase the priority of the application in the task manager. On Windows, the application in the foreground has implicitly higher priority than that in the background, so even focusing other windows may have negative impact.
You can also close unneeded applications, delay automatic updates, or restart the computer for stopping processes, you even don’t know about.